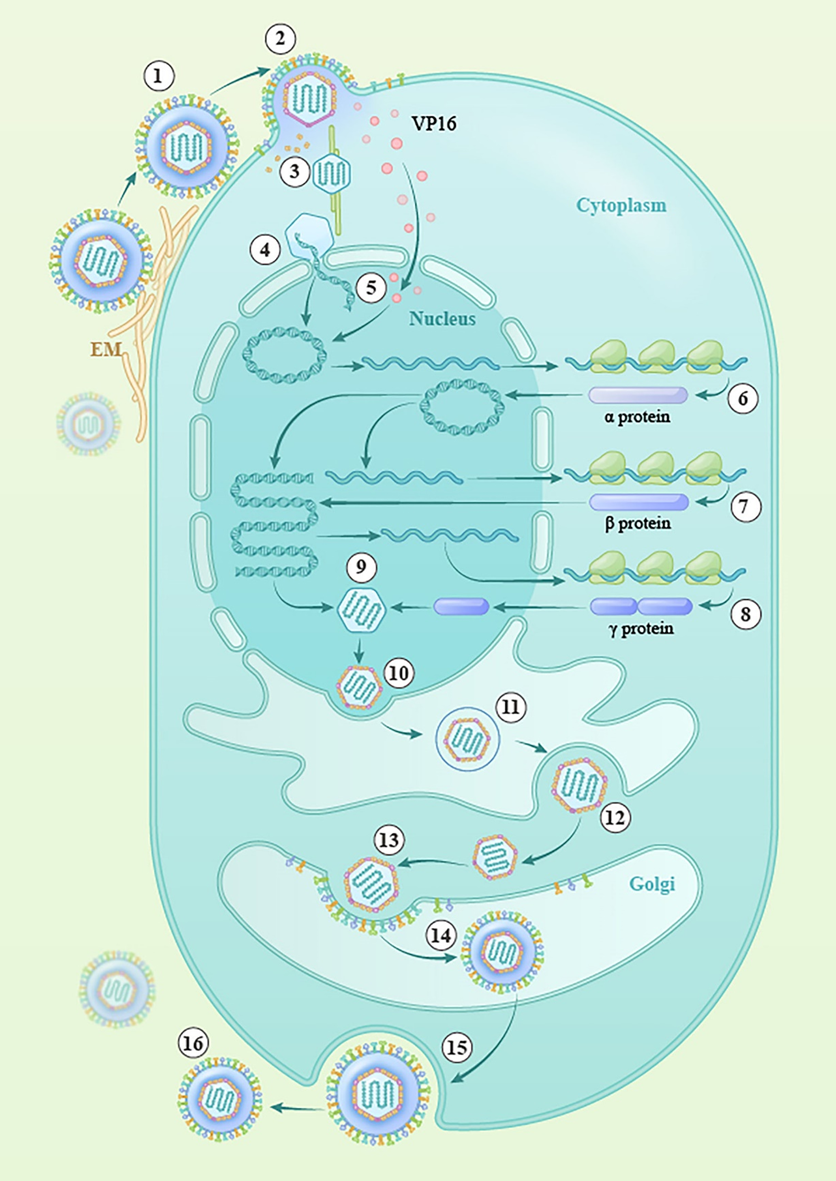
Herpesviruses are a family of double-stranded DNA viruses with a tegument structure and a genome composed of a single sequence and terminal repeat sequences. The herpesvirus UL14 gene encodes the protein UL14 (pUL14), which has various subcellular localizations, plays critical roles in regulating immediate-early gene transcription and expression, influences the intracellular localization patterns of a number of proteins belonging to the capsid and the DNA packaging machinery, participates in secondary envelopment, and influences viral particle release. Additionally, pUL14 has roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing apoptosis. This review discusses how pUL14 participates in the life cycle of herpesviruses and provides new ideas for further research on pUL14 function in viral infection.
The related research has been published in the Frontiers in Microbiology under the title " Multiple functions of the herpesvirus UL14 gene product in viral infection," and is accessible at the following DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1483022