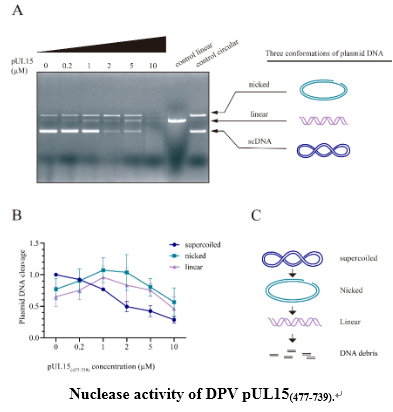
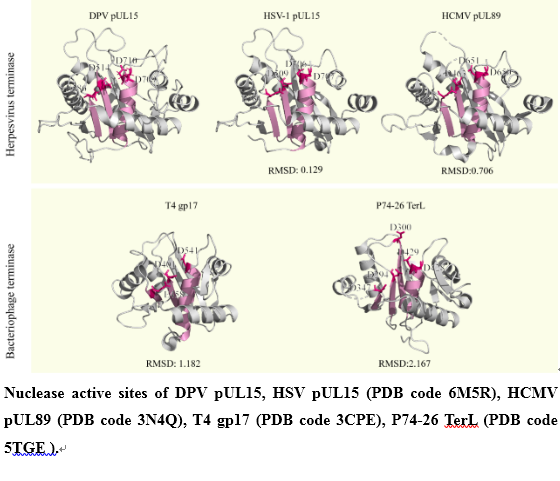
Duck plague virus (DPV), also known as anatid herpesvirus, is a double-stranded DNA virus and a member of α herpesvirus. DPV pUL15 is a homolog of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) pUL15 which is terminase large subunit and plays a key role in the cleavage and packaging of the viral concatemeric genome. However, the sequence similarity between DPV pUL15 and its homologues is low and it is not sure if DPV pUL15 has the potential to cleave the concatemeric genome as same as its homologues. Here, we expressed the C terminal domain of DPV pUL15 to explore the nuclease function of DPV pUL15. The main results showed that DPV pUL15 C-terminal domain has a nonspecific nuclease activity. DPV pUL15 nuclease activity needs to coordinate with divalent metal ions and tends to be more active at high temperatures. Even though the structure of DPV pUL15 nuclease domain is relatively conserved, the mutations of conserved amino acids on the nuclease domain do not significantly inhibit the nuclease activity.
The results were published in Veterinary Microbiology, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2023.109671